Hubs and switches function as a common connection point for the workstations, printers, file servers and other devices that make up a network. The main difference between hubs and switches is the way in which they communicate with the network.
What is a Hub?
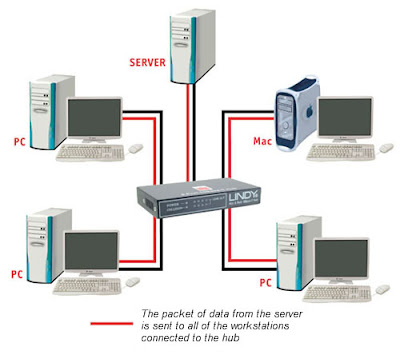
A hub functions as the central connection point of a network. It joins together the workstations, printers, and servers on a network, so they can communicate with each other. Each hub has a number of ports that connect it to the other devices via a network cable.
How does a Hub work?
A hub is an inexpensive way to connect devices on a network. Data travels around a network in 'packets' and a hub forwards these data packets out to all the devices connected to its ports.
As a hub distributes packets to every device on the network, when a packet is destined for only one device, every other device connected to the hub receives that packet. Because all the devices connected to the hub are contending for transmission of data the individual members of a shared network will only get a percentage of the available network bandwidth. This process can slow down a busy network.
A 10Base-T hub Ethernet Hub provides a total of 10 Mbit/sec of bandwidth, which all users share. If one person on the network is downloading a very large file, for example, little or no bandwidth is available for other users. These users will experience very slow network performance.
What is a Switch?
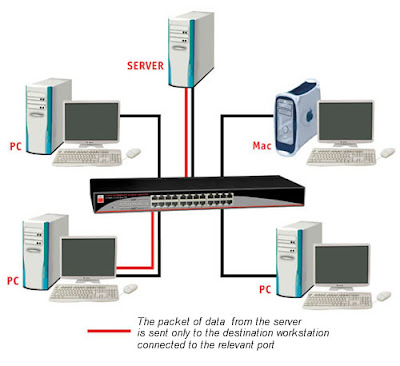
A switch is more sophisticated than a hub, giving you more options for network management, as well as greater potential to expand. A switch filters the data packets, and only sends the packet to the port which is connected to the destination address of that packet. It does this by keeping a table of each destination address and its port. When the switch receives a packet, it reads the destination address and then establishes a connection between the source port and the destination port. After the packet is sent, the connection is terminated.
What are the advantages of a Switch?
A switch provides higher total throughput than a hub because it can support multiple simultaneous conversations. For example, when a 100Mbit/sec hub has five workstations, each receives only 20Mbit/sec of the available bandwidth. When a 10-100Mbit/sec switch is used every port on the switch represents a dedicated 100Mbit/sec path, so each workstation receives 100Mbit/sec of bandwidth.
Switches also run in full duplex mode, which allows data to be sent and received across the network at the same time. Switches can effectively double the speed of the network when compared to a hub which only supports half duplex mode.
Why choose one of our Switches?
Switches improve the performance and efficiency of a network and should be used when you:
- Need to make best use of the available bandwidth
- Have multiple file servers
- Require improved performance from file servers, web servers or workstations
- Use high speed multi-media applications
- Are adding a high speed workgroup to a 10Mbit/sec LAN
- Plan to upgrade from 10 to 100Mbit/sec or Gigabit network
The standard features on all N-Way switches are:
- 10-100Mbit/sec Auto-Negotiation on all ports, the switch automatically senses the speed of the attached device and configures the port for the proper speed. This simplifies deployment in mixed Ethernet and Fast Ethernet environments
- Auto MDI/MDI-X auto-detects whether the connected cable type is normal or cross-over
- Full or Half Duplex operation